Streaming Jobs
Twister2 supports streaming jobs to be developed using two APIs.
- Compute API
- TSet API
Compute API is similar to the Apache Storm API and TSet API is similar to the Apache Flink API. Compute API is more versatile compared to the TSet API and streaming applications are natural fit for this API. TSet API provides a typed API for streaming.
Streaming job is modeled as a graph which contains sources, computations and links. Every graph starts with sources and can have multiple computations linked together. The links represent a communication (messaging) between the sources, and computations.
A user programs an streaming applications by providing implementations of sources, computations and linking them together using the communication mechanisms provided by the APIs.
Lets take the word count example, which is used as a hello world example in big data applications.
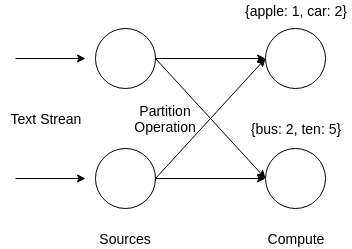
In this example, set of sources read data from an incoming text stream. A hashed based routing is used to send the words to a correct compute task. At this point a global count of a word can be calculated because each word goes to its corresponding task every time.
Compute API
Lets look at how this graph can be created and executed with Twister2 using the compute API.
ComputeEnvironment cEnv = ComputeEnvironment.init(config, workerID,
workerController, persistentVolume, volatileVolume);
// create source and aggregator
WordSource source = new WordSource();
WordAggregator counter = new WordAggregator();
// build the graph
ComputeGraphBuilder builder = ComputeGraphBuilder.newBuilder(config);
builder.addSource("word-source", source, 4);
builder.addCompute("word-aggregator", counter, 4)
.partition("word-source")
.viaEdge("aggregate")
.withDataType(MessageTypes.OBJECT);
builder.setMode(OperationMode.STREAMING);
// build the graph
ComputeGraph graph = builder.build();
// execute graph
cEnv.getTaskExecutor().execute(graph);
Above is only the graph creation and execution part. Please refer to the full example in word count the source code for more details.
In the above example we create two tasks, one is the source task called WordSource and other is the
compute task called WordAggregator. These two tasks are added to ComputeGraphBuilder and connected by the partition edge (link).
The partition edge, by default uses hash of the message to select the destination of a message.
TSet API
Here is the same example with the TSet API.This example can be found in the source code word count.
StreamingTSetEnvironment cEnv = TSetEnvironment.initStreaming(WorkerEnvironment.init(config,
workerID, workerController, persistentVolume, volatileVolume));
// create source and aggregator
cEnv.createSource(new SourceFunc<String>() {
// sample words
private List<String> sampleWords = new ArrayList<>();
// the random used to pick he words
private Random random;
@Override
public void prepare(TSetContext context) {
this.random = new Random();
RandomString randomString = new RandomString(MAX_CHARS, random, RandomString.ALPHANUM);
for (int i = 0; i < NO_OF_SAMPLE_WORDS; i++) {
sampleWords.add(randomString.nextRandomSizeString());
}
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return true;
}
@Override
public String next() {
return sampleWords.get(random.nextInt(sampleWords.size()));
}
}, 4).partition(new HashingPartitioner<>()).sink(new SinkFunc<String>() {
// keep track of the counts
private Map<String, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
private TSetContext context;
@Override
public void prepare(TSetContext context) {
this.context = context;
}
@Override
public boolean add(String word) {
int count = 1;
if (counts.containsKey(word)) {
count = counts.get(word);
count++;
}
counts.put(word, count);
LOG.log(Level.INFO, String.format("%d Word %s count %s", context.getIndex(),
word, count));
return true;
}
});
// start executing the streaming graph
cEnv.run();
Streaming Operators
Twister2 supports following streaming operations. More information of these operations can be found int compute API.
| Operations | Description |
|---|---|
| Direct | A one to one mapping from a task to to another |
| Reduce | Reduce values from N tasks to a single task |
| AllReduce | Reduce values from N tasks and distributes to M tasks |
| Gather | Gathers values from N tasks to a single task |
| AllGather | Gathers values from N tasks and distributes to M tasks |
| Broadcast | Broadcast a value from 1 task to N tasks |
| Partition | All to all operation that sends values from N tasks to M tasks |
| Keyed-Partition | All to all operation that sends values from N tasks to M tasks according to a key |