Multistage
Multistage Example
Multistage example refers to one or more intermediate tasks between the source and sink task.
Batch Tasks
private static class GeneratorTask extends BaseStreamSource {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -254264903510284748L;
private int count = 0;
@Override
public void execute() {
if (count == 999) {
if (context.writeEnd("partition-edge", "Hello")) {
count++;
}
} else if (count < 999) {
if (context.write("partition-edge", "Hello")) {
count++;
}
}
}
}
private static class ReduceTask extends BaseStreamSink {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -254264903510284791L;
private int count = 0;
@Override
public boolean execute(IMessage message) {
count++;
LOG.info(String.format("%d %d Reduce received count: %d", context.getWorkerId(),
context.taskId(), count));
return true;
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private static class PartitionTask extends BaseStreamCompute {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -254264903510284798L;
private int count = 0;
@Override
public boolean execute(IMessage message) {
if (message.getContent() instanceof Iterator) {
Iterator it = (Iterator) message.getContent();
while (it.hasNext()) {
count += 1;
context.write("compute-edge", it.next());
}
}
LOG.info(String.format("%d %d Partition Received count: %d", context.getWorkerId(),
context.taskId(), count));
return true;
}
}
Stream Task
private static class GeneratorTask extends BaseStreamSource {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -254264903510284748L;
private int count = 0;
@Override
public void execute() {
if (count == 999) {
if (context.writeEnd("partition-edge", "Hello")) {
count++;
}
} else if (count < 999) {
if (context.write("partition-edge", "Hello")) {
count++;
}
}
}
}
private static class ReduceTask extends BaseStreamSink {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -254264903510284791L;
private int count = 0;
@Override
public boolean execute(IMessage message) {
count++;
LOG.info(String.format("%d %d Reduce received count: %d", context.getWorkerId(),
context.taskId(), count));
return true;
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private static class PartitionTask extends BaseStreamCompute {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -254264903510284798L;
private int count = 0;
@Override
public boolean execute(IMessage message) {
if (message.getContent() instanceof Iterator) {
Iterator it = (Iterator) message.getContent();
while (it.hasNext()) {
count += 1;
context.write("compute-edge", it.next());
}
}
LOG.info(String.format("%d %d Partition Received count: %d", context.getWorkerId(),
context.taskId(), count));
return true;
}
}
In the multistage example we have a source task, two compute tasks which extends the BaseCompute class. There can be multiple compute tasks depending on the description of the task. In this one we generate a stream of data in the source task and in the intermediate task the partition is done and in the final task we do a reduction operation.
public void execute() {
GeneratorTask g = new GeneratorTask();
ReduceTask rt = new ReduceTask();
PartitionTask r = new PartitionTask();
TaskGraphBuilder builder = TaskGraphBuilder.newBuilder(config);
builder.addSource("source", g, 4);
ComputeConnection pc = builder.addCompute("compute", r, 4);
pc.partition("source", "partition-edge", DataType.OBJECT);
ComputeConnection rc = builder.addCompute("sink", rt, 1);
rc.reduce("compute", "compute-edge", new IFunction() {
@Override
public Object onMessage(Object object1, Object object2) {
return object1;
}
});
builder.setMode(OperationMode.STREAMING);
DataFlowTaskGraph graph = builder.build();
TaskUtils.execute(config, allocatedResources, graph, workerController);
}
Here the ComputeConnection class calls the reduce function to reduce the data via the compute task to the sink task.
Run the following command to run this example.
To run Multistage Batch Example
./bin/twister2 submit standalone jar examples/libexamples-java.jar edu.iu.dsc.tws.examples.task.batch.MultiStageGraph
MultiStage TaskGraph Batch Source Code
To run Multistage Streaming Example
./bin/twister2 submit standalone jar examples/libexamples-java.jar edu.iu.dsc.tws.examples.task.streaming.MultiStageGraph
MultiStage TaskGraph Streaming Source Code
Multiple Compute Tasks Example
The multiple compute tasks consists of a source node and sends output to multiple compute dataflow nodes. Also, the final compute task receive the input from multiple compute dataflow nodes.
The structure of the graph is given below:
Source (Task 1)
|
|
V
Task2 Task3 (Multiple Compute Elements)
| |
| |
V V
Target (Task 4)
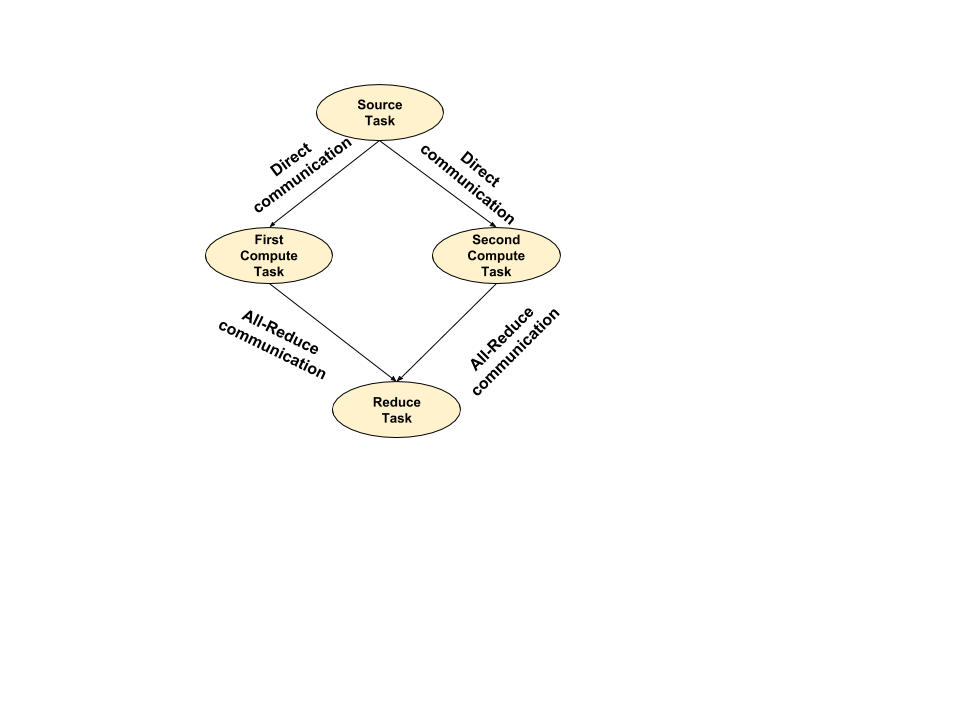
Multiple Compute Tasks Example
This example is described in four stages namely
- defining the task graph
- creating the compute connections
- creating the communication edges between the compute connections
- build and execute the task graph
SourceTask sourceTask = new SourceTask();
FirstComputeTask firstComputeTask = new FirstComputeTask();
SecondComputeTask secondComputeTask = new SecondComputeTask();
ReduceTask reduceTask = new ReduceTask();
builder.addSource("source", sourceTask, parallel);
ComputeConnection firstComputeConnection = builder.addCompute(
"firstcompute", firstComputeTask, parallel);
ComputeConnection secondComputeConnection = builder.addCompute(
"secondcompute", secondComputeTask, parallel);
ComputeConnection reduceConnection = builder.addCompute("compute", reduceTask, parallel);
The source task creates the direct communication edge beween the first compute and second compute task. From the first compute and second compute, it creates an all-reduce communication edge to the reduce task.
firstComputeConnection.direct("source", "fdirect", DataType.OBJECT);
secondComputeConnection.direct("source", "sdirect", DataType.OBJECT);
reduceConnection.allreduce("firstcompute", "freduce", new Aggregator(), DataType.OBJECT);
reduceConnection.allreduce("secondcompute", "sreduce", new Aggregator(), DataType.OBJECT);
This build and generate the task graph for the batch process. Then, it call the taskscheduler and taskexecutor to build the task schedule plan and execution plan respectively. Finally, it calls the execute method to execute the generated task graph.
builder.setMode(OperationMode.BATCH);
DataFlowTaskGraph graph = builder.build();
ExecutionPlan plan = taskExecutor.plan(graph);
taskExecutor.execute(graph, plan);
To Run Multiple Compute Tasks Example
./bin/twister2 submit standalone jar examples/libexamples-java.jar edu.iu.dsc.tws.examples.internal.taskgraph.MultiComputeTasksGraphExample -dsize 100 -parallelism 2 -workers 2 -dim 2 -csize 4 -dinput /tmp/dinput -cinput /tmp/dinput -filesys local -nFiles 1